|
|
Greece & Greek Culture Educational Posters & Prints, pg 1/2
for the classroom, home schoolers, decor for office.
|
social studies > geography > Europe > GREECE 1 | 2 < Ancient Greek Civilization
|
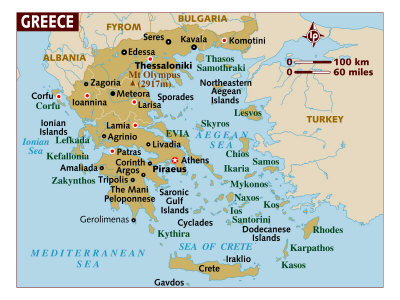
Modern day Greece, officially known as the Hellenic Republic, is located on the southern end of Europe's southeastern Balkan peninsula and numerous islands in the surrounding Aegean Sea (east) and the Ionia Sea (west). Greece is bordered by Turkey to the east, Albania, Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north.
Greece has a long and rich history and is considered the birthplace of Western civilization with the advent of democracy, philosophy, literature, and art. There is evidence of human presence as early as 70,000 years ago, the pre-Hellenic Bronze Age Minoan (2600-1450 BC) and Mycenaen (1600-1100 BC) cultures, the rise of the city-states, and Alexander the Great's unification of the Greek Empire to the Hellenistic Era of the spread of Greek culture to the surrounding region.
|
|
|
|
|
Athens, the capital and largest city of Greece is one of the world's oldest cities, having been continuously inhabited for at least 7000 years, with its recorded history spanning around 3,400 years. Athens sits on the Attica peninsula which projects into the Aegean Sea. Athens takes its name from the goddess Athena.
Classical Athens was a powerful city-state and a center for the arts, learning and philosophy, the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum, and is called the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy.
The Acropolis of Athens, a high flat topped rock, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The most famous temple on the Acropolis is the Parthenon, built in the 5th century BC.
Notable people associate with Athens include Aeschylus, Aristophanes, Euripides, Herodotus, Phidias, Plato, Socrates, Solon, Sophocles, Thucydides, Xenophon.
• architectural posters
|
|
|
|
Argos, Greece, located on the Peloponnese, is one of the most ancient cities of the world. It was a major settlement during the Mycenaean period, and during the classical Greek period Argos was a rival of Sparta.
The most notable ancient monument in the city today is the renowned Heraion of Argos.
Most Ancient European Towns Network: Argos, Beziers, Cadiz, Colchester, Cork, Evora, Maastricht, Roskilde, Tongeren, Worms.
|
|
|
|
The site of ancient Corinth, a city-state on the Isthmus of Corinth, was occupied as early as the Neolithic period.
The Greek myths inform us that the city was found by Corinthos who descended from Helios, the Sun.
Paul wrote two letter, epistles, to the Christian community at Corinth (1 & II Corinthians).
|
|
|
|
Eleusis (Eleusina) is best known for having been the site of the Eleusinian Mysteries, one of the most famous religious events of the ancient Greeks.
Today Eleusina is a major industrial center, with the largest oil refinery in Greece.
Notable people associated with Eleusis include Aeschylus.
|
|
|
|
Ephesus was an ancient Greek city, and later a major Roman city, located on the west coast of Asia Minor, near present-day Selçuk, Izmir Province, Turkey.
During the Classical Greek ere Ephesus was one of the twelve cities of the Ionian League; in the Roman period (1st century BC), Ephesus had a population of more than 250,000 makinge it one of the largest cities in the Mediterranean world.
Ephesus was an important center of Early Christianity, with Paul living and writing in Ephesus (the book of Ephesians).
Notable people associated with Eleusis include Heraclitus.
|
|
|
|
Epidaurus was the birthplace of Apollo's son Asclepius, the god of medicine and healing. The theatre at Epidaurus was built from the proceeds of the many people who visited seeking a cure for their illness.
• Aesculapius & Hippocrates
|
|
|
|
In the second millennium BC Mycenae, as a military stronghold dominating much of southern Greece, was one of the major centers of Greek civilization.
|
|
|
|
Rhodes, Greece, on the island of Rhodes, is remembered as the site of the Colossus of Rhodes, a 107 ft statue of the sun god Helios.
The Colossus, one of the original Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, stood at the harbor entrance for 56 years before being destroyed in an earthquake c. 226 BC.
|
|
|
|
The ancient city-state of Sparta, Greece, is noted for its unique social structure based on military training. Located in south-eastern Peloponnese, in the area called Lacedaemon, a landscape that is a natural fortress.
In Greek mythology Sparta was the daughter of Eurotas and Clete, and the wife of Lacedaemon who was the son of Zeus and the Pleaid Taygete.
The adjective “spartan” is used to suggest “simplicity, frugality, or avoidance of luxury and comfort”. The term “laconic” describes the terse and concise way of speaking that was characteristic of the Spartans.
|
|
|
|
The Grecian city Thebes, on the Boeotian plain, played an important role in Greek mythology as the setting of stories of Cadmus, Oedipus and Dionysus.
Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed an early Mycenaean settlement; at one time a major rival of Athens, Thebes was destroyed by Alexander the Great in 335 BC.
Notable people associated with Thebes include the poet Pindar, whose house was not destroyed by Alexander.
|
|
|
|
Thessaloniki, Greece's second major economic, industrial, commercial, political, and transportation center, is also renowned for its festivals, events and vibrant cultural life.
The city has a history of over 2,300 years: its Byzantine and Christian monuments have been declared a UNESCO World Heritage site.
|
|
|
|
One of the largest volcanic eruptions on Earth, of the Santorini Volcano, destroyed the civilization and it was only rediscovered at the beginning of the 20th century, and named after the mythical King Minos and the labyrinth.
Afterwards, Mycenaean Greek culture became dominant at Minoan sites in Crete.
|
|
|
|
Mount Olympus, the highest mountain in Greece, was considered the home of the gods by the Ancient Greeks.
• more Olympic posters |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A Bronze Age civilization arose on the island of Crete and flourished from approximately 2700 to 1450 BC. • more mask posters |
|
|
|
Ulysses and His Companions Gouging Out the Eye of the Cyclops Polyphemus
• explorers posters
|
|
|
|
Bust of Pericles, statesman, orator & general
c.430 BC, (Marble Roman copy of a Greek original)
|
|
|
|
Marble kouros, so-called Strangford Apollo possibly Cyclades, c.500 BC
|
|
|
|
The Euthydikos Kore, from the Acropolis, c.490 BC (marble)
|
|
|
|
Statue of Hermes and the Infant Dionysus, c.330 BC, Praxiteles
|
|
|
|
|
|
previous page | top | GREECE 1 | 2 < Ancient Greek Civilization
|
|
I have searched the web for visual, text, and manipulative curriculum support materials - teaching posters, art prints, maps, charts, calendars, books and educational toys featuring famous people, places and events - to help teachers optimize their valuable time and budget.
Browsing the subject areas at NetPosterWorks.com is a learning experience where educators can plan context rich environments while comparing prices, special discounts, framing options and shipping from educational resources.
Thank you for starting your search for inspirational, motivational, and educational posters and learning materials at NetPosterWorks.com. If you need help please contact us.
|
|
|
|
|