|
|
Earth's Fractured Surface Map
for oceanography and marine geology science, environmental, ecology, and geography educators.
|
science > geography > landforms > FRACTURED EARTH MAP < geology < social studies
|
|
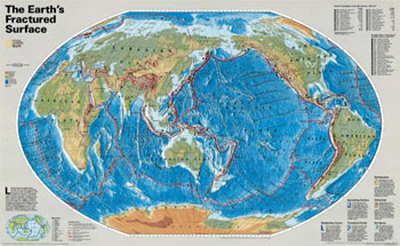
The Earth's Fractured Surface Map Art Print
|
Like the pieces of a giant jigsaw puzzle, slabs of rocky crust known as tectonic plates fit together to form the Earth's outer shell. The puzzle changes as the plates slide over the hotter, softer rocks beneath them. Moving by mere inches annually, they reshape continents and ocean basins over millions of years by colliding, separating, and scraping past one another with relentless force. These interactions set off earthquakes, fire-up volcanoes, and wrinkle the Earth's crust into mountains, valleys, and deep-sea trenches.
SUBDUCTION ZONES: When two plates collide, one oftern dives beneath the other–a process called subduction. Oceanic plates subduct under continents and perhaps under other oceanic plates as well, forming trenches that mark their descent. Where continental plates run into each other, they buckle, creating ranges such as the Himalaya.
SPREADING CENTERS: As tectonic plates move apart, magma rises in the resulting rift, hardens, and is pulled aside, making way for more magma. Under the oceans this process has created the 46,000-mile-long Mid-Ocean Ridge system, segmented by faults, that snakes around the globe. On land the process has created–and contines to widen–the East African Rift System.
TRANSFORM FAULTS: Sometimes tectonic plates shift past each other horizontally at a boundary known as a transform fault–a distinct type of strike-slip fault. The San Andreas, one example, accommodates movement fitfully along its several hundred miles–slow creep in some places, frequently small jumps or rare big ones in others.
EARTHQUAKES: Most quakes occur near plate boundaries, where rock grinds past rock. Friction keeps the plate edges from sliding smoothly. The longer they remain stuck, the more strain builds and the more violent the snap and resulting vibrations–the earthquake. ...
VOLCANOES: Magma rises to the surface from inside the Earth mainly at subduction zones and spreading centers. The edge of the Pacific Basin–the 30,000-mile-long Ring of Fire–is especially volatile, with about 70 percent of the world's more than 500 historically active volcanoes. ...
HOT SPOTS: In a scattering of places, magma burns through a tectonic plate. Each hot spot likely marks the top of a plume of semimolten rock that rises many hundreds of miles inside the Earth. As a plate slowly pases above, the plume melts into it, creating a chain of volcanoes such as those in the Hawaiian Islands.
|
|
|
|
World Physical Map of the Ocean Floor
|
|
|
|
Endangered Earth Map
National Geographic map pinpoints the growing threats to the delicate balance between development and natural regeneration of the planet.
• ecology/environoment posters
• Central image world map showing the physical earth and oceans
• World map insets showing the Ice Age vegetation 18,000 years ago, and Greeenhouse-effect vegetation zones
• A timeline, entitled, “People and planet: a troubled partnership. Graphic shows population growth from 16,000 BC to the present, demonstrating how advances in agriculture and public health have enabled the human race to burgeon–and over-populate the Earth”.
• Descriptions of growing threats, including population pressure, air and water pollution, rise in ozone levels, species extinctions, and more
• Inset showing a Peru-Ecuador upwelling, illustrating how rapidly the oceans can change
• Inset showing Minnesota's Boreal Forest, and the pressures on it from human intervention
Coverage Area: The World, North America, South America, Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, Oceania, Antarctica
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
previous page | top
|
|
I have searched the web for visual, text, and manipulative curriculum support materials - teaching posters, art prints, maps, charts, calendars, books and educational toys featuring famous people, places and events - to help teachers optimize their valuable time and budget.
Browsing the subject areas at NetPosterWorks.com is a learning experience where educators can plan context rich environments while comparing prices, special discounts, framing options and shipping from educational resources.
Thank you for starting your search for inspirational, motivational, and educational posters and learning materials at NetPosterWorks.com. If you need help please contact us.
|
|
|